Reading Time: 8 minutes
Thinning of hair and balding takes a toll on the self-confidence of a person. Our Fashion and Beauty expert, Shameena, tells us about hair grafting, in detail. Here’s her in-depth research, in the weekly column, exclusively for Different Truths.
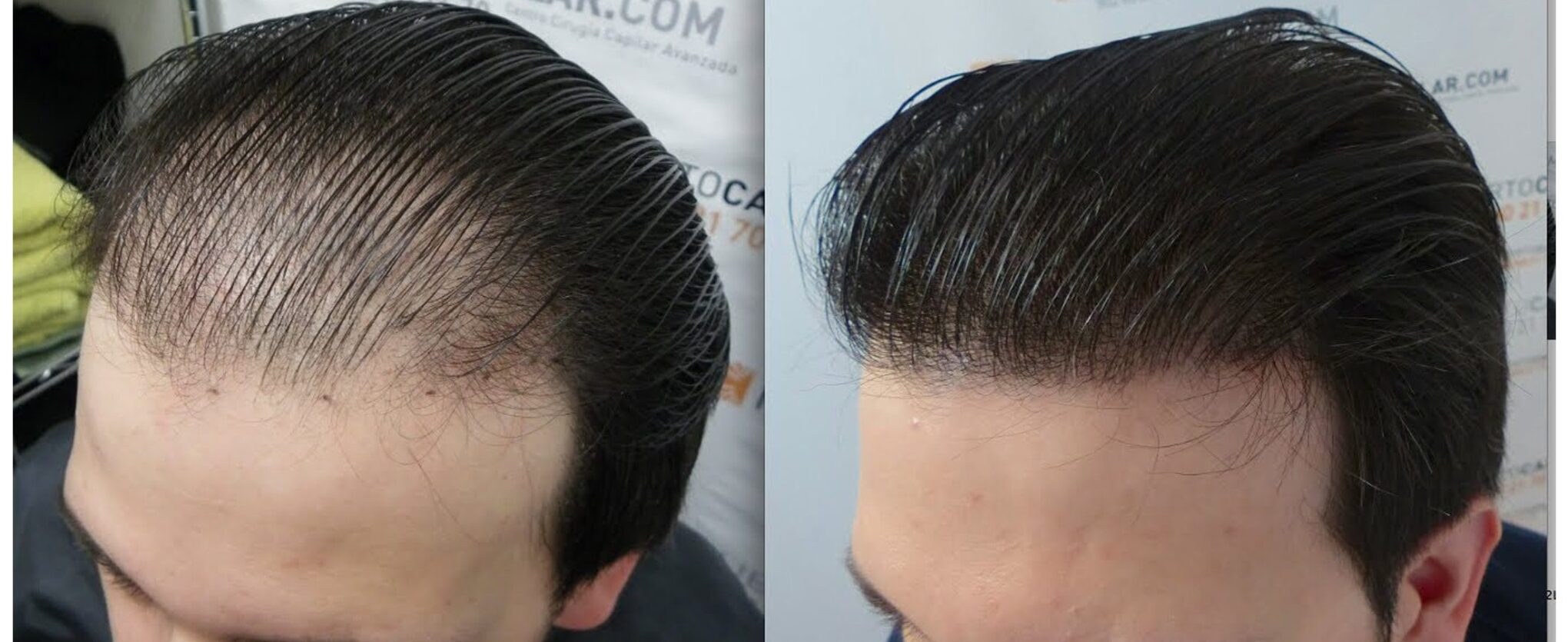
Like good health and youth, most of us take our locks for granted – that is, until they’re gone. For many people, a hair transplant can help bring back what looks like a full – or at least a fuller – head of hair.
Hair transplant is the latest craze not only for those who have lost their hair to untimely fall but even for them who want to alter their hairlines or acquire an attractive mane. If thinning up top or going bald really bothers you, the procedure can be one way to feel more confident about your looks.
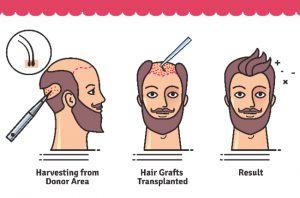
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that removes hair follicles from one part of the body, called the ‘donor site’, to a bald or balding part of the body known as the ‘recipient site’. The technique is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness. In this minimally invasive procedure, grafts containing hair  follicles that are genetically resistant to balding, (like the back of the head) are transplanted to the bald scalp. Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, and pubic hair and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants.
follicles that are genetically resistant to balding, (like the back of the head) are transplanted to the bald scalp. Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, and pubic hair and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants.
Hair transplantation differs from skin grafting in that grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis surrounding the hair follicle, and many tiny grafts are transplanted rather than a single strip of skin.
Since hair naturally grows in groupings of 1 to 4 hairs, current techniques harvest and transplant hair “follicular units” in their natural groupings. Thus, modern hair transplantation can achieve a natural appearance by mimicking original hair orientation. This hair transplant procedure is called follicular unit transplantation (FUT). Donor hair can be harvested in two different ways: strip harvesting, and follicular unit extraction (FUE).
Here are the steps:
- Preparation for the Hair Transplant: In the initial step of the hair transplant surgery, hair follicles from the back of the head are removed and relocated to the balding areas.
- Donor Area Trimmed: Before the surgery is started, the hair in the donor area is trimmed.
- Donor Area Prepared for Surgery: Once the hair in the donor area is trimmed it is given local anaesthesia.
- Tissue in the Donor Area Removed and the Donor Area Sutured: The tissue in the donor area that contains the bald resistant hair follicles is then removed surgically and the donor area is sutured.
- Combed Hair over Sutured Donor Area: The sutures in the donor area are hidden from the patient’s hair that is combed over them. These sutures are removed almost ten days after the hair transplant surgery.
- Donor Tissue Trimmed into Follicular Unit Grafts: Microscopes are then used by the surgical technicians to view the donor tissue for dissecting and preparing follicular units for hair grafts.
- Bald Recipient Area Prepared: Once the local anaesthesia is given to the patient, the balding recipient area is prepared for the surgical process No trimming/removal of hair is required at the top of the recipient area.
- Incisions Made in the Balding Areas: Follicular Unit Grafts are placed in the tiny incisions that are made in an irregular pattern in the recipient area.
- Grafts Placed According to Densities: The smallest grafts (one and two) are placed in front of the hairline and three and four (denser than one and two) are placed behind.
- Immediately after the Hair Transplant Surgery: After the hair transplant surgery, tiny incisions with short hair would be visible on the patient’s operated area.
- The closing of the Hair Transplant Surgery: The incision marks heal naturally and the redness in the recipient area vanishes itself within a week.
Harvesting Methods
Transplant operations are performed on an outpatient basis, with mild sedation (optional) and injected local anaesthesia. The scalp is shampooed and then treated with an antibacterial agent prior to the donor scalp being harvested.
There are several different techniques for harvesting hair follicles, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Regardless of the harvesting technique, proper extraction of the hair follicle is paramount to ensure the viability of the transplanted hair and avoid transection, the cutting of the hair shaft from the hair follicle. Hair follicles grow at a slight angle to the skin’s surface, so transplanted tissue must be removed at a corresponding angle.
There are two main ways in which donor grafts are extracted today: strip excision harvesting, and follicular unit extraction.
Strip Harvesting
Strip harvesting is the most common technique for removing hair and follicles from a donor site. The surgeon harvests a strip of skin from the posterior scalp, in an area of good hair growth. A single-, double-, or triple-bladed scalpel is used to remove strips of hair-bearing tissue from the donor site. Each incision is planned so that intact hair follicles are removed. The excised strip is about 1–1.5 x 15–30 cm in size. While closing the resulting wound, assistants begin to dissect individual follicular unit grafts, which are small, naturally formed groupings of hair follicles, from the strip. Working with binocular Stereo-microscopes, they carefully remove excess fibrous and fatty tissue while trying to avoid damage to the follicular cells that will be used for grafting. The latest method of closure is called ‘Trichophytic closure’, which results in much finer scars at the donor area.
The surgeon then uses very small micro blades or fine needles to puncture the sites for receiving the grafts, placing them in a predetermined density and pattern, and angling the wounds in a consistent fashion to promote a realistic hair pattern. The technicians generally do the final part of the procedure, inserting the individual grafts in place.
Strip harvesting will leave a thin linear scar in the donor area, which is typically covered by a patient’s hair even at relatively short lengths. The recovery period is around 2 weeks and will require the stitches/staples to be removed by medical personnel or subcuticular suturing can be done.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
With Follicular Unit Extraction or FUE harvesting, individual follicular units containing 1 to 4 hairs are removed under local anaesthesia; this micro removal typically uses tiny punches of between 0.6mm and 1.0mm in diameter. The surgeon then uses very small micro blades or fine needles to puncture the sites for receiving the grafts, placing them in a predetermined density and pattern, and angling the wounds in a consistent fashion to promote a realistic hair pattern. The technicians generally do the final part of the procedure, inserting the individual grafts in place.
FUE takes place in a single long session or multiple small sessions. The FUE procedure is more time 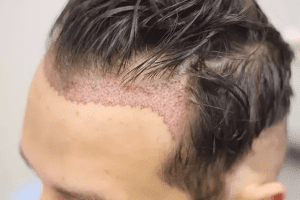 consuming than strip surgery. An FUE surgery time varies according to the surgeon’s experience, speed in harvesting and patient characteristics. The procedure can take anywhere from a couple hours to extract 200 grafts for a scar correction to a surgery over two consecutive days for a mega session of 2,500 to 3,000 grafts. With the FUE Hair Transplant procedure, there are restrictions on patient candidacy. Clients are selected for FUE based on a fox test, though there is some debate about the usefulness of this in screening clients for FUE.
consuming than strip surgery. An FUE surgery time varies according to the surgeon’s experience, speed in harvesting and patient characteristics. The procedure can take anywhere from a couple hours to extract 200 grafts for a scar correction to a surgery over two consecutive days for a mega session of 2,500 to 3,000 grafts. With the FUE Hair Transplant procedure, there are restrictions on patient candidacy. Clients are selected for FUE based on a fox test, though there is some debate about the usefulness of this in screening clients for FUE.
FUE can give very natural results. The advantage over strip harvesting is that FUE harvesting negates the need for large areas of scalp tissue to be harvested, so there is no linear incision on the back of the head and it doesn’t leave a linear scar. Because individual follicles are removed, only small, punctate scars remain which are virtually not visible and any post-surgical pain and discomfort is minimised. As no suture removal is required, recovery from Micro-Grafting FUE is less than 7 days.
Disadvantages include increased surgical times and higher cost to the patient. It is challenging for new surgeons because the procedure is physically demanding and the learning curve to acquire the skills necessary is lengthy and tough. Some surgeons note that FUE can lead to a lower ratio of successfully transplanted follicles as compared to strip harvesting.
Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT)
Follicular unit transplant (FUT) is the traditional hair transplant method which involves extracting a linear strip of hair-bearing skin from the back or the side of the scalp. The strip is then dissected to separate individual grafts.
Expectations and Recovery
After the surgery, your scalp may be very tender. You may need to take pain medications for several days. Your surgeon will have you wear bandages over your scalp for at least a day or two. He may also prescribe an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory drug for you to take for several days. Most people are able to return 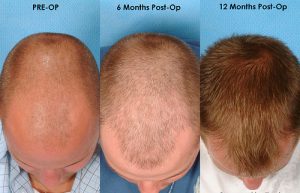 to work 2 to 5 days after the operation.
to work 2 to 5 days after the operation.
Within 2 to 3 weeks after surgery, the transplanted hair will fall out, but you should start to notice new growth within a few months. Most people will see 60% of new hair growth after 6 to 9 months. Some surgeons prescribe the hair-growing drug minoxidil (Rogaine) to improve hair growth after transplantation, but it’s not clear how well it works.
Hair transplant is a non-invasive procedure and is on several occasions done on an outpatient basis. Most patients are allowed to shampoo after two or three days although the scalp needs to be protected from sun and infections for a while after the surgery. The patients are generally put on antibiotics for a few days.
Fact Sheet about Hair Transplant
1) The transplanted hair behaves like natural hair and sheds between two to four weeks of transplant. The roots thereafter start sprouting hair naturally and continue to do so for a lifetime.
2) Use of local anaesthesia makes it a painless procedure and the patient can go home the same day.
3) Hair transplant is different from non-surgical hair restoration in which a pre-chosen base is fixed on the scalp with dexterity.
4) Hair transplant does not mean you will have a luxurious crop of hair as the result varies from person to person and has also some link to a person’s natural hair quality.
5) Every case of baldness does not have a solution in hair transplantation. It entirely depends on case to case basis.
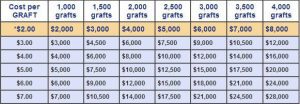
6) The cost of the procedure depends on the number of grafts. The more the number of grafts, the higher the cost.
Hair Graft Calculator
It helps you identify the areas where you feel more hair is needed.
The graft calculator will allow you to gain a rough idea of the number of grafts and hairs that will be needed for the procedure. Once you’ve got an idea of the number of grafts needed you’ll be able to request your hair transplant cost from the clinic.
Risks and Costs of Treatment
The price of a hair transplant will depend largely on the amount of hair you’re moving, but it generally ranges from $4,000 to $15,000. Most insurance plans don’t cover it.
As with any kind of surgery, transplants have some risks, including bleeding and infection. There’s also the chance for scarring and unnatural-looking new hair growth.
Around the time new locks start to grow, some people have inflammation or an infection of the hair follicles, called folliculitis. Antibiotics and compresses can relieve the problem. It’s also possible to suddenly lose some of the original hair in the area where you got the new strands, called shock loss. But most of the time, it’s not permanent.
©Shameena Abdurahiman
Photos from the Internet
#HairGrafting #AnswerToHairLoss #GrowYourOwnHair #HairSurgery #HarvestingHair #HairTreatment #FashionFunda #DifferentTruths

















nice post shared.